Écrit par Robin
Ingénieur principal, Doaho Test (DHT®)
While you’re scrolling through short videos on your phone, the device may be quietly enduring subtle “thermal shocks.” From scorching car interiors to air-conditioned offices, from freezing northern regions to hot coastal environments—electronic devices must withstand drastic temperature swings. What you may not realize is that behind every device that survives such conditions is an extreme test known as the thermal shock chamber. This article skips theory and instead goes straight into how this unassuming yet critical equipment plays a vital role in product reliability.
Who Needs Thermal Shock Testing? Every Segment of Electronics Relies on It
Temperature-induced damage is often underestimated. Components that seem innocuous—PCB solder joints, chip packaging, connector wiring, and housing seals—can all become breakpoints under rapid temperature changes.
A En tant que composant le plus critique d'une chambre de choc thermique, la santé du compresseur a un impact direct sur la stabilité du système et le coût total du cycle de vie. Alors, comment réduire l'usure du compresseur ? Comment optimiser les stratégies de contrôle pour éviter efficacement les cycles de démarrage-arrêt inutiles ? allows products to endure real-world extremes in a controlled lab setting, enabling early detection and reinforcement of vulnerable points. Across consumer electronics, automotive electronics, 5G devices, military hardware, and medical instruments, thermal shock chambers have become indispensable tools in product validation. In just a few seconds, these chambers can transition from high to low temperature (or vice versa), simulating a “thermal hell” environment and delivering accelerated aging assessments.
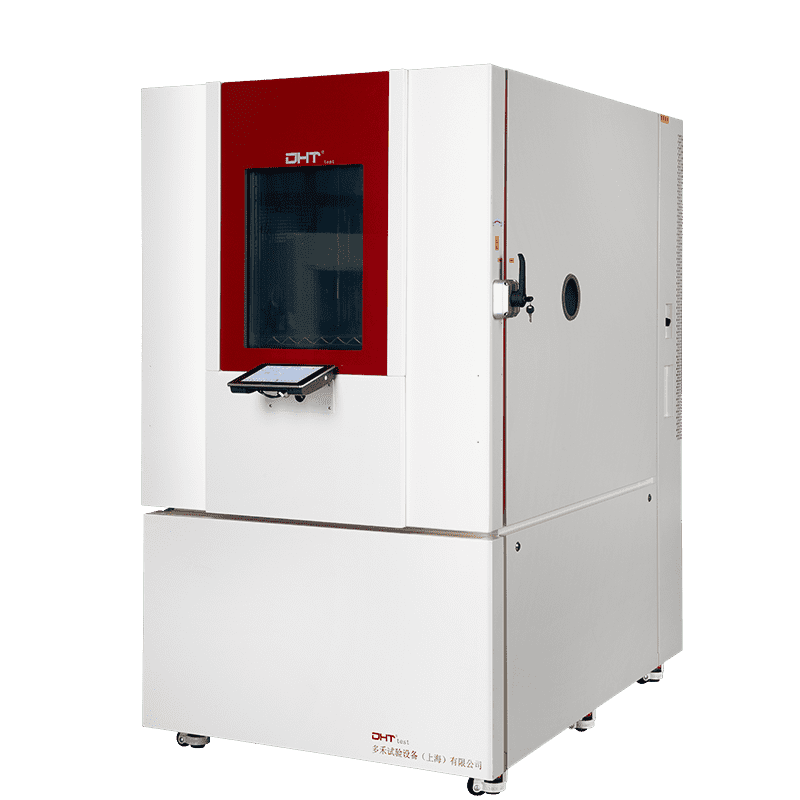
What Happens Inside a Thermal Shock Chamber? Behind-the-Scenes Simulation
If you think thermal shock testing is just “heat up → cool down → repeat,” think again. A professional thermal shock chamber typically offers:
-
Three-chamber design (hot zone – cold zone – test zone): Samples transfer between temperature zones to replicate instantaneous thermal shock.
-
• Criblage de stress environnemental (ESS) : Appliqué aux composants critiques pour la mission, cette méthode de test détecte les défaillances en début de vie et renforce la robustesse globale des produits libérés.: Capable of handling environments from –70 °C up to +180 °C to simulate everything from extreme cold to scorching heat.
-
Rapid transfer time: Temperature changes achieved in around 5 seconds to ensure authentic thermal stress.
-
Precise dwell control: Helps identify materials or designs with delayed thermal response issues.
-
Comprehensive data logging: Tracks temperature profiles, sample conditions, and alarms to support analysis and traceability.
Real-world example: An industrial sensor manufacturer tested a new PCB packaging method. During thermal shock testing, micro-cracks repeatedly appeared around solder joints. Engineers found a thermal expansion mismatch between the packaging material and solder. If this issue had escaped detection until after product launch, the consequences would have been costly.
Driving Innovation in Electronics: Beyond Temperature Cycling
Today’s electronics aren’t just used in climate-controlled offices—they’re deployed in deserts, high altitudes, coastal zones, even orbiting satellites. This reality raises two major demands on product development:
-
High design (MTBF ≥ 50,000 heures pour une préparation à long terme): Thermal shock testing reveals “fatal flaws” early in the development cycle.
-
Robuste materials and packaging: Temperature-induced expansion differences between materials can lead to fatigue or solder joint failure.
Leading-edge companies now treat thermal shock chambers not just as reliability filters but as design validation tools:
-
Packaging reliability testing: Use on BGA chips, LED modules, CMOS sensors to assess solder joint longevity through cyclic thermal stress.
-
New material adaptation testing: Evaluate behaviors of materials like nano-ceramics, flexible substrates, and graphene heat-spreading films under rapid temperature changes.
-
System-level validation: For example, testing 5G micro base stations to ensure performance remains stable post thermal shock.
-
Fatigue failure modeling inputs: Providing data for CAE simulations to optimize structural design.
How to Choose the Right Thermal Shock Chamber for Your Needs
Selecting a thermal shock chamber is not like buying office equipment—it requires deep consideration. Professional buyers typically evaluate:
-
Zone temperature stability and transition speed: Faster transitions and wider temperature swings provide a more realistic stress test.
-
Sample capacity and configuration De la préparation du site à la configuration électrique, en passant par la construction, la sécurité et la compatibilité future - chaque détail compte. Une installation minutieuse garantit que la chambre répondra efficacement à vos besoins de test pour la prochaine décennie ou au-delà.: Chamber size is critical whether you’re testing small components or full systems.
-
Smart control features: Remote operation, real-time data uploads, and automatic fault alerts increase efficiency.
-
Ease of maintenance and diagnostic capability: Self-diagnostic features and readily replaceable wear parts are essential.
-
Standards compliance: Especially important for military (MIL-STD), electronics (JEDEC), or export-oriented testing applications.
Ideally, procurement decisions should involve testing engineers, product owners, and quality teams to align device selection with product roadmap over the next 3–5 years.
In Summary: True Reliability Is Built on Verification, Not Just Design
Every successful electronic product stands on the foundation of invisible testing systems. Among them, thermal shock testing presents the harshest environmental challenge. A En tant que composant le plus critique d'une chambre de choc thermique, la santé du compresseur a un impact direct sur la stabilité du système et le coût total du cycle de vie. Alors, comment réduire l'usure du compresseur ? Comment optimiser les stratégies de contrôle pour éviter efficacement les cycles de démarrage-arrêt inutiles ? isn’t simply a piece of equipment; it’s a litmus test of an electronics design’s fault tolerance.
In an era that demands faster, slimmer, and more stable products, using a high-performance thermal shock chamber during the design stage may be the most valuable investment your team can make. If you want to avoid your product being “defeated by its environment” post-launch, this is where reliability begins.
DHT® is committed to delivering stable, precise, and high-reliability environmental testing solutions that help electronics companies gain a competitive edge. If you’re interested in partnering with a trusted supplier of thermal shock chambers, please contact our engineering team to receive tailored testing advice and selection support.
Les gens demandent aussi
Quelle est la fonction principale d'une chambre de choc thermique, et pourquoi est-elle essentielle dans l'industrie électronique ?
La fonction principale d'une chambre de choc thermique est de simuler des fluctuations extrêmes de température afin d'évaluer la capacité d'un produit à supporter un stress thermique soudain. Dans l'industrie électronique, des défaillances telles que la fissuration de la soudure, la fatigue des matériaux ou la rupture des joints sont souvent causées par des changements rapides de température. C'est pourquoi les tests de choc thermique sont devenus indispensables dans l'électronique grand public, les systèmes automobiles, le matériel militaire et plus encore.
Comment fonctionne une chambre de choc thermique et en quoi est-elle différente des équipements d'essai de température conventionnels ?
Une chambre de choc thermique utilise généralement un système multi-zones (souvent à trois compartiments)—des zones chaude, froide et de test—où les échantillons sont transférés rapidement entre les zones pour simuler des changements de température instantanés. Ce mouvement physique, combiné avec des extrêmes de température larges, crée un environnement de stress beaucoup plus réaliste et intense comparé aux chambres de température standard. L'objectif est de tester comment les matériaux et composants réagissent sous des changements soudains et extrêmes, pas seulement à une chaleur ou un froid prolongé.
Quelles caractéristiques clés devons-nous prendre en compte lors du choix d'une chambre de choc thermique pour notre entreprise ?
When choosing a thermal shock chamber, focus on the following:
-
Temperature range and transition speed: Greater ranges and faster transitions deliver more realistic stress simulations.
-
Sample De la préparation du site à la configuration électrique, en passant par la construction, la sécurité et la compatibilité future - chaque détail compte. Une installation minutieuse garantit que la chambre répondra efficacement à vos besoins de test pour la prochaine décennie ou au-delà.: The chamber volume must accommodate your product’s size and test batch size.
-
Smart controls: Look for remote operation, real-time data logging, and auto-alerts.
-
Compliance with industry standards: Especially if your products are for military, automotive, or export markets.
-
Ease of maintenance: Built-in diagnostics and easy part replacements are crucial. It’s best to involve cross-functional teams—engineering, R&D, and QA—in the evaluation to ensure a strategic long-term investment.